This section provides technological resources for developers of Lima.
See also Community » Contributing
for how to contribute to the project.
This is the multi-page printable view of this section. Click here to print.
This section provides technological resources for developers of Lima.
See also Community » Contributing
for how to contribute to the project.
${LIMA_HOME})Defaults to ~/.lima.
Note that we intentionally avoid using ~/Library/Application Support/Lima on macOS.
We use ~/.lima so that we can have enough space for the length of the socket path,
which must be less than 104 characters on macOS.
Unix: The directory can not be located on an NFS file system, it needs to be local.
${LIMA_HOME}/_config)The config directory contains global lima settings that apply to all instances.
User identity:
Lima creates a default identity and uses its public key as the authorized key
to access all lima instances. In addition, lima will also configure all public
keys from ~/.ssh/*.pub as well, so the user can use the ssh endpoint without
having to specify an identity explicitly.
user: private keyuser.pub: public key${LIMA_HOME}/<INSTANCE>)An instance directory contains the following files:
Metadata:
lima-version: the Lima version used to create this instancelima.yaml: the YAMLprotected: empty file, used by limactl protectcloud-init:
cloud-config.yaml: cloud-init configuration, for reference only.cidata.iso: cloud-init ISO9660 image. See cidata.iso.Ansible:
ansible-inventory.yaml: the Ansible node inventory. See ansible.disk:
image: the downloaded VM image; renamed to disk or iso during setupimage.ipsw: hardlink to image, created for running VZMacOSInstaller that requires the image file to have the .ipsw suffixdisk: the VM disk (can be a symlink to legacy diffdisk)iso: optional CDROM image for ISO-based installations (can be a symlink to legacy basedisk)basedisk: legacy name for the downloaded image (pre-v2.1 instances; may remain as a qcow2 backing file)diffdisk: legacy name for disk (pre-v2.1 instances)disk mount:
mnt: the mount point directory for the disk, used for macOS guestskernel:
kernel: the kernelkernel.cmdline: the kernel cmdlineinitrd: the initrdQEMU:
qemu.pid: QEMU PIDqmp.sock: QMP socketqemu-efi-code.fd: QEMU UEFI code (not always present)VZ:
vz.pid: VZ PIDvz-identifier: Unique machine identifier file for a VMvz-hwmodel: Hardware model information for a Mac VMvz-aux: Auxiliary storage for a Mac VMvz-efi: EFIVariable store file for a VMSerial:
serial.log: default serial log (QEMU only), for debuggingserial.sock: default serial socket (QEMU only), for debugging (Usage: socat -,echo=0,icanon=0 unix-connect:serial.sock)serialp.log: PCI serial log (QEMU (ARM) only), for debuggingserialp.sock: PCI serial socket (QEMU (ARM) only), for debugging (Usage: socat -,echo=0,icanon=0 unix-connect:serialp.sock)serialv.log: virtio serial log, for debuggingserialv.sock: virtio serial socket (QEMU only), for debugging (Usage: socat -,echo=0,icanon=0 unix-connect:serialv.sock)SSH:
ssh.sock: SSH control master socketssh.config: SSH config file for ssh -F. Not consumed by Lima itself.VNC:
vncdisplay: VNC display host/portvncpassword: VNC display passwordGuest agent:
Each drivers use their own mode of communication
qemu: uses virtio-port io.lima-vm.guest_agent.0vz: uses vsock port 2222wsl2: uses free random vsock port
The fallback is to use port forward over ssh portga.sock: Forwarded to /run/lima-guestagent.sock in the guest, via SSHHost agent:
ha.pid: hostagent PIDha.sock: hostagent REST APIha.stdout.log: hostagent stdout (JSON lines, see pkg/hostagent/events.Event)ha.stderr.log: hostagent stderr (human-readable messages)${LIMA_HOME}/_disk/<DISK>)A disk directory contains the following files:
data disk:
datadisk: the qcow2 or raw disk that is attached to an instancelock:
in_use_by: symlink to the instance directory that is using the diskWhen using vmType: vz (Virtualization.framework), on boot, any qcow2 (default) formatted disks that are specified in additionalDisks will be converted to RAW since Virtualization.framework only supports mounting RAW disks. This conversion enables additional disks to work with both Virtualization.framework and QEMU, but it has some consequences when it comes to interacting with the disks. Most importantly, a regular macOS default cp command will copy the entire virtual disk size, instead of just the used/allocated portion. The easiest way to copy only the used data is by adding the -c option to cp: cp -c old_path new_path. cp -c uses clonefile(2) to create a copy-on-write clone of the disk, and should return instantly.
ls will also only show the full/virtual size of the disks. To see the allocated space, du -h disk_path or qemu-img info disk_path can be used instead. See #1405 for more details.
${LIMA_HOME}/_templates)The templates directory can store additional template files that can be referenced with the template: schema.
If the template directory exists (and $LIMA_TEMPLATES_PATH is not set), then this directory will be searched before the /usr/local/share/lima/templates default directory that contains all the templates bundled with Lima itself.
~/Library/Caches/lima)Currently hard-coded to ~/Library/Caches/lima on macOS.
Uses $XDG_CACHE_HOME/lima, normally $HOME/.cache/lima, on Linux.
Uses %LocalAppData%\lima, C:\Users\<USERNAME>\AppData\Local\lima, on Windows.
~/Library/Caches/lima/download/by-url-sha256/<SHA256_OF_URL>)The directory contains the following files:
url: raw url text, without “\n”data: data<ALGO>.digest: digest of the data, in OCI format.
e.g., file name sha256.digest, with content sha256:5ba3d476707d510fe3ca3928e9cda5d0b4ce527d42b343404c92d563f82ba967The instance directory contains an inventory file, that might be used with Ansible playbooks and commands. See Building Ansible inventories about dynamic inventories.
cidata.isocidata.iso contains the following files:
user-data: Cloud-init user-datameta-data: Cloud-init meta-datanetwork-config: Cloud-init Networking Config Version 2lima.env: The LIMA_CIDATA_* environment variables (see below) available during boot.sh processingparam.env: The PARAM_* environment variables corresponding to the param settings from lima.yamllima-guestagent: Lima guest agent binarynerdctl-full.tgz: nerdctl-full-<VERSION>-<OS>-<ARCH>.tar.gzboot.sh: Boot scriptboot.<OS>/*: Boot script modulesboot.essential.<OS>/*: Essential boot script modules, executed in plain mode too.util/*: Utility command scripts, executed in the boot script modulesprovision.data/*: Custom provision files (data)provision.dependency/*: Custom provision scripts (dependency)provision.system/*: Custom provision scripts (system)provision.user/*: Custom provision scripts (user)provision.yq/*: Custom provision scripts (yq)etc_environment: Environment variables to be added to /etc/environment (also loaded during boot.sh)Max file name length = 30
The volume label is “cidata”, as defined by cloud-init NoCloud.
LIMA_CIDATA_DEBUG: the value of the --debug flag of the limactl start command.LIMA_CIDATA_IID: the instance ID, regenerated on every boot.LIMA_CIDATA_NAME: the lima instance nameLIMA_CIDATA_MNT: the mount point of the disk. /mnt/lima-cidata.LIMA_CIDATA_USER: the username stringLIMA_CIDATA_UID: the numeric UIDLIMA_CIDATA_COMMENT: the full name or comment stringLIMA_CIDATA_HOME: the guest home directoryLIMA_CIDATA_SHELL: the guest login shellLIMA_CIDATA_HOSTHOME_MOUNTPOINT: the mount point of the host home directory, or empty if not mountedLIMA_CIDATA_MOUNTS: the number of the Lima mountsLIMA_CIDATA_MOUNTS_%d_MOUNTPOINT: the N-th mount point of Lima mounts (N=0, 1, …)LIMA_CIDATA_MOUNTTYPE: the type of the Lima mounts (“reverse-sshfs”, “9p”, …)LIMA_CIDATA_DATAFILE_%08d_OVERWRITE: set to “true” if the datafile should be overwritten if it already exists.LIMA_CIDATA_DATAFILE_%08d_OWNER: set to the owner of the datafile.LIMA_CIDATA_DATAFILE_%08d_PATH: set to the path the datafile should be copied to.LIMA_CIDATA_DATAFILE_%08d_PERMISSIONS: set to the file permissions (in octal) for the datafile.LIMA_CIDATA_CONTAINERD_USER: set to “1” if rootless containerd to be set upLIMA_CIDATA_CONTAINERD_SYSTEM: set to “1” if system-wide containerd to be set upLIMA_CIDATA_CONTAINERD_ARCHIVE: the name of the containerd archive. nerdctl-full.tgzLIMA_CIDATA_SLIRP_GATEWAY: set to the IP address of the host on the SLIRP network. 192.168.5.2.LIMA_CIDATA_SLIRP_DNS: set to the IP address of the DNS on the SLIRP network. 192.168.5.3.LIMA_CIDATA_SLIRP_IP_ADDRESS: set to the IP address of the guest on the SLIRP network. 192.168.5.15.LIMA_CIDATA_UDP_DNS_LOCAL_PORT: set to the udp port number of the hostagent dns server (or 0 when not enabled).LIMA_CIDATA_TCP_DNS_LOCAL_PORT: set to the tcp port number of the hostagent dns server (or 0 when not enabled).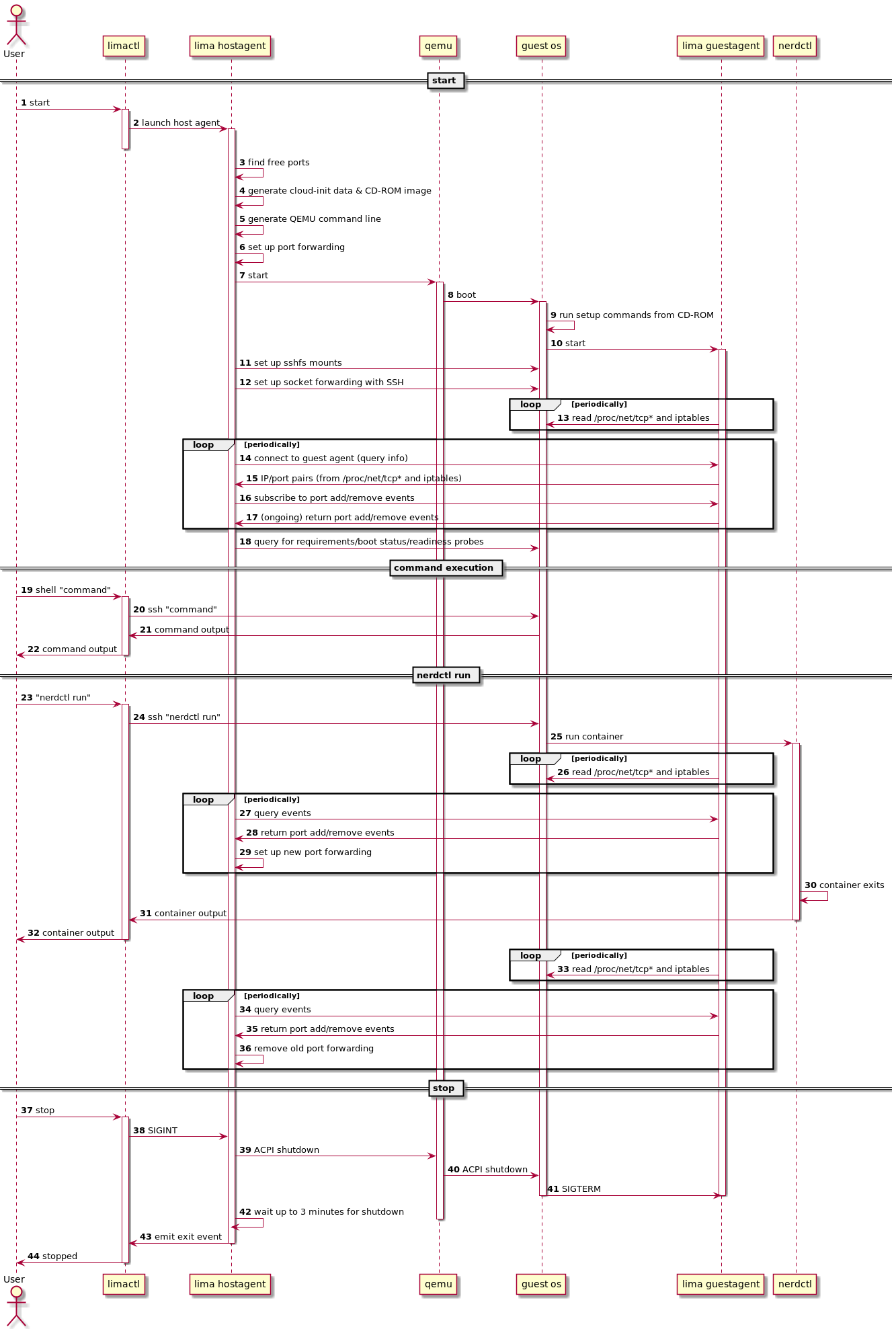
(based on Lima 0.8.3)
| ⚡ Requirement | Lima >= 2.0 |
|---|
Lima supports two types of drivers: internal and external. This architecture allows for extensibility and platform-specific implementations. Drivers are unware whether they are internal or external.
💡 See also: VM Types for user configuration of different virtualization backends.
Internal Drivers are compiled directly into the limactl binary and are registered automatically at startup by passing the driver object into registry.Register() function and importing the package in the main limactl code using Go’s blank import _. For example:
Build tags control which drivers are compiled as internal vs external (e.g., external_qemu, external_vz, external_wsl2).
External Drivers are separate executables that communicate with Lima via gRPC. They are discovered at runtime from configured directories.
⚠️ Note: External drivers are experimental and the API may change in future releases.
You can build existing internal drivers as external drivers using the ADDITIONAL_DRIVERS Makefile variable:
# Build QEMU as external driver
make ADDITIONAL_DRIVERS=qemu limactl additional-drivers
# Build multiple drivers as external
make ADDITIONAL_DRIVERS="qemu vz wsl2" limactl additional-drivers
This creates external driver binaries in _output/libexec/lima/ with the naming pattern lima-driver-<name> (or lima-driver-<name>.exe on Windows).
Lima discovers external drivers from these locations:
LIMA_DRIVERS_PATH environment variable<LIMA-PREFIX>/libexec/lima/, where <LIMA_PREFIX> is the location path where the Lima binary is presentThe discovery process is handled by pkg/registry/registry.go.
To create a new external driver:
driver.Driver interface:type Driver interface {
Lifecycle
GUI
SnapshotManager
GuestAgent
Info() Info
Configure(inst *limatype.Instance) *ConfiguredDriver
FillConfig(ctx context.Context, cfg *limatype.LimaYAML, filePath string) error
SSHAddress(ctx context.Context) (string, error)
}
server.Serve() to expose your driver:package main
import (
"context"
"github.com/lima-vm/lima/v2/pkg/driver/external/server"
)
func main() {
driver := &MyDriver{}
server.Serve(context.Background(), driver)
}
Build and deploy:
go build -o lima-driver-mydriver main.goLIMA_DRIVERS_PATHUse the driver: Explicitly specify the driver when creating instances:
limactl create myinstance --vm-type=mydriver template:default
See existing external driver implementations:
The unit tests are written in Go and can be executed with the following commands:
go test -v ./...
The unit tests do not execute actual virtual machines.
The integration tests incurs actual execution of virtual machines.
The integration tests are written in BATS (Bash Automated Testing System).
Run the following commands to run the BATS tests:
git submodule update --init --recursive
make bats
The BATS tests are located under hack/bats/tests.
There are also extra tests (hack/bats/extras) that are not automatically
invoked from make bats.
Run the following command to run the extra BATS tests:
./hack/bats/lib/bats-core/bin/bats ./hack/bats/extras
Tests that are specific to template files are written in bash and partially in Perl.
Use hack/test-templates.sh
to execute tests, with a virtual machine template file, e.g.,:
./hack/test-templates.sh ./templates/default.yaml
./hack/test-templates.sh ./templates/fedora.yaml
./hack/test-templates.sh ./hack/test-templates/test-misc.yaml
.github/workflows/test.yml
executes the tests on the GitHub Actions with the “Tier 1” templates.
Most tests are executed on Linux runners, as macOS runners are slow and flaky.
The tests about macOS-specific features (e.g., vz and vmnet) are still executed on macOS runners.
Currently, the Intel version of macOS is used, as the ARM version of macOS on GitHub Actions still do not support nested virtualization.
Lima uses BATS with the bats-support, bats-assert, and bats-file helper libraries.
All tests run with errexit enabled (via BATS_RUN_ERREXIT=1 in
helpers/load.bash), so any failing command aborts the test immediately.
runUse run only when you need to capture output or assert a non-zero exit code.
Do not use it just to check that a command succeeds.
Call the command directly. errexit handles the failure case.
# Good
limactl shell "$INSTANCE" -- mkdir -p /tmp/foo
# Bad — unnecessary run and status check
run limactl shell "$INSTANCE" -- mkdir -p /tmp/foo
[[ $status == 0 ]]
# Bad — unnecessary run and assert_success
run limactl shell "$INSTANCE" -- mkdir -p /tmp/foo
assert_success
Use run -0 to assert success and capture $output/$lines, then use
assert_output or assert_line to verify the output.
# Good
run -0 limactl shell "$INSTANCE" -- cat /tmp/hello.txt
assert_output "hello"
# Bad — manual status and output checks
run limactl shell "$INSTANCE" -- cat /tmp/hello.txt
[[ $status == 0 ]]
[[ $output == "hello" ]]
Use run -N where N is the expected exit code.
run -1 limactl yq -n foo
assert_output --partial "invalid input"
Use run_e (a wrapper for run --separate-stderr) when you need to check
both stdout and stderr. The helpers assert_fatal, assert_warning,
assert_info, assert_error, and assert_debug match Lima’s structured
log output in stderr.
run_e -1 limactl ls foo foobar bar
assert_warning 'No instance matching foobar found.'
assert_fatal 'unmatched instances'
Use bats-file assertions instead of test expressions.
# Good
assert_file_exists "$LIMA_HOME/$INSTANCE/protected"
assert_dir_exists "$BATS_TEST_TMPDIR/foo/bar"
# Bad — raw test expressions give poor failure messages
[[ -f "$LIMA_HOME/$INSTANCE/protected" ]]
[[ -d "$BATS_TEST_TMPDIR/foo/bar" ]]
Define local_setup_file, local_teardown_file, local_setup, and
local_teardown instead of overriding setup_file, setup, etc. directly.
The base implementations in helpers/load.bash call these local_ variants
automatically.
Set INSTANCE at file scope to have setup_file create (or reuse) a Lima
instance and teardown_file delete it.
| Goal | Pattern |
|---|---|
| Command must succeed, ignore output | limactl ... (bare command) |
| Command must succeed, check output | run -0 cmd; assert_output ... |
| Command must fail | run -N cmd; assert_output ... |
| Command must fail, check stderr | run_e -N cmd; assert_fatal ... |
| Command must succeed, check stderr | run_e -0 cmd; assert_info ... |
| File or directory exists | assert_file_exists / assert_dir_exists |
To combine multiple commits into one (recommended unless your PR covers multiple topics):
# Adjust the number based on how many commits you want to squash
git rebase -i HEAD~3
In the interactive editor that appears:
pickpick to fixup (short formf). You may also choose squash (s), however, fixup is recommended to keep the commit message clean.Example:
pick aaaaaaa First commit message
pick bbbbbbb Second commit message
pick ccccccc Fix typo
To:
pick aaaaaaa First commit message
f bbbbbbb Second commit message
f ccccccc Fix typo
To update your branch with the latest changes from upstream:
git remote add upstream https://github.com/lima-vm/lima.git # Only needed once
git fetch upstream
git rebase upstream/master
If you encounter issues during rebase:
git rebase --abort # Cancel the rebase and return to original state
git status # Check current state
For merge conflicts during rebase:
git add the resolved filesgit rebase --continue